
Cryptocurrency and the blockchain technology it’s built on can be really difficult to understand.
It’s cloaked in over-complicated technical jargon and surrounded by a cult-like following of investors that endorse cryptocurrency as the future of the financial world.
Meanwhile, there are hordes of financial experts on the other side of the fence that denounce crypto as nothing but overhyped digital nonsense.
So, to properly understand cryptocurrency we need to ask some basic questions:
- What is cryptocurrency?
- How does it work?
- Which cryptocurrency should you buy?
This comprehensive, jargon-free guide will help you cut through the noise surrounding cryptocurrency and give you a detailed analysis of all the core themes — so that you can make the best, informed decisions about whether or not investing in Bitcoin, Ethereum or any of the other cryptocurrencies is the right choice for you.
In This Comprehensive Guide
What Is Cryptocurrency?
If you run a quick google search asking for the definition of: “cryptocurrency” — this is what comes up:
“A digital currency in which transactions are verified and records are maintained by a decentralized system using cryptography, rather than by a centralized authority.”
Not overly helpful…
Much More Simply:
- A cryptocurrency is a code-based digital asset that sits on top of a network of computers that are distributed throughout the world.
- This is called decentralization.
- This decentralized structure allows them to exist outside the control of governments and central authorities like banks. Decentralization ultimately means that cryptocurrencies do not originate from one location, nor is there a governing body that can make decisions about who can access it.
- The complex computing systems that power cryptocurrency and make them incredibly secure are called blockchains.
- Blockchains record, verify and store all the transactions that occur on its system. They are also called distributed ledgers. A ledger is simply a record of transactions. All traditional banks record transactions when you buy and sell stuff, it’s just that a cryptocurrency’s ledger is public (therefore transparent) and is split up and stored throughout a network of computers around the world.
Unlike paper & digital money, which are the regular dollars that populate your wallet and the numbers on the screen of your bank account, cryptocurrency is almost impossible to counterfeit because blockchains are extremely difficult to hack or change.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
To understand how a cryptocurrency works, you have to understand the basics of blockchain. The blockchain technology that cryptocurrencies are built on is the fundamental property that gives cryptocurrencies real value as assets.
Whether or not a cryptocurrency has a sufficiently decentralized, robust, and efficient blockchain will determine the future success of that cryptocurrency.
Here’s how blockchain works, explained in the most straightforward way possible:
- A blockchain is a database shared across a network of computers.
- Users record their transactions on this database.
- Once a record has been added to that network it’s practically impossible to alter.
- To guarantee that no one has come in and changed any of the entries in the database, the network makes constant checks to make sure that all of the records are the same.
Here’s what an everyday transaction looks like on a blockchain:
Step One
- A transaction or trade is made between two parties and the record of this is stored inside a block.
- The record lists the details of the transaction and contains a signature from each party.
Step Two
- The record is added to the network and checked by other computers.
- The computers in the network, called ‘nodes’, check the details of the trade to make sure that it is valid.
Step Three
- The records that the network accepts as valid are then added to a block.
- Each block contains a unique code called a hash code (which is visualised as the added # in the diagram below). Each block also contains the hash code of the previous block in the chain.
- The block is then added to the blockchain. These new hash codes connect the blocks together in a specific order.
Hash Codes
A hash code is created by a mathematical function that takes digital information and generates a string of letters and numbers from it.
Let’s take a closer look at two important characteristics of hash codes:
First, no matter what the size of the original file, a hash function will always generate a code of the same length. For example, a tweet that I make on Twitter is much shorter than the Bible, but they would both have hash codes of the same length.
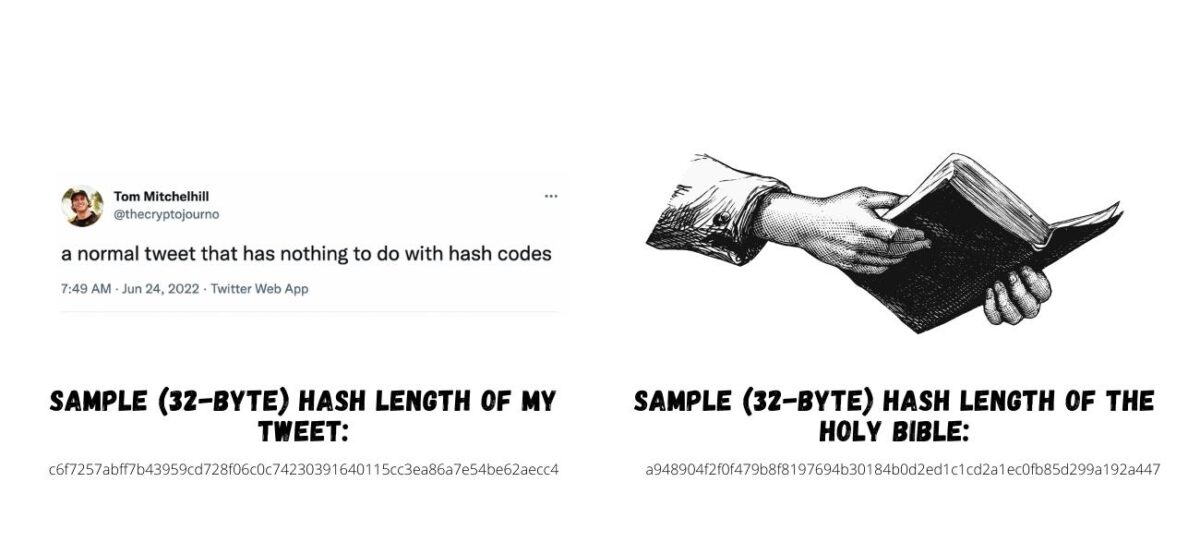
Secondly, and most importantly — any change to the original input will generate a new hash. So, if someone decided to delete a single letter from anyone of the Bible’s 783,137 words, it would show up, because the new hash code would change entirely.
Hash Codes Keep Blockchain Secure
- As we’ve just learned: a changed hash code breaks the chain.
- The next block in the chain still has the old hash, so to restore the functionality of the chain a hacker would have to alter that one too. And the next one, and the next one, and so on.
- Recalculating all those hashes would take an enormous amount of computing power. Like evil genius supercomputer level power.
Even if you were capable of taking over the Frontier supercomputer in the US and wield its awesome 8.7 million cores of processing power, it’s still pretty much impossible to successfully attack a sufficiently decentralized blockchain.
The 2 Types of Blockchain: Explained
Now that we’ve gotten the real nitty gritty of blockchain out of the way, let’s take a look at the two main models of blockchain that cryptocurrencies can use:
- Proof of Work: This is used by Bitcoin & Ethereum.
- Proof of Stake: This is used by Cardano & Binance Coin.
In simple terms, Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are two different ways that you can mine cryptocurrencies.
Proof of Work
This model that requires computers to solve extremely complex cryptographic problems in order to generate new cryptocurrency and validate the transactions on the blockchain. This is what people are referring to when they use the term “mining”, because the computers are quite literally doing lots of work to create new cryptocurrency, the same way that physical labour is used to dig minerals out of the ground.
The upside of this model is that it guarantees an extremely secure blockchain network, constantly validated and secured by massive amounts of raw computing power. In order to hack a Proof of Work system the hacker would have to have a computer or more aptly, thousands of computers that are more powerful than 51% of the total network. This makes Proof of Work incredibly secure.
The downside to this, is that it requires dizzying amounts of computing power to mine new crypto and validate the transactions on the network. To put this in perspective, Bitcoin mining currently uses the same amount of energy as Argentina…
Proof of Stake
The Proof of Stake model, in very simple terms, only requires computers to validate new blocks rather than actually “mining” them, although the term mining is still used when talking about Proof of Stake. This stakeholder validation method is a good deal faster and uses substantially less energy. It is one of the largest and most obvious differentiators that you should consider when looking at a cryptocurrency.
If you’re mining a Proof of Stake cryptocurrency, the system temporarily takes a sizeable chunk of your cryptocurrency for a few seconds and uses that as a form of insurance whilst validating and recording transactions. If you were a malicious hacker seeking to alter the blockchain, your cryptocurrency would be immediately taken from you and it would disappear back into the network as a consequence. This heavily incentivizes users to make sure they’re doing the right thing, or they’re guaranteed to lose a massive chunk of their holdings.
To ensure long term security on the blockchain, an algorithm randomly selects which nodes and stakeholders can become validators for each block so that participants are unable to intentionally utilise large sums of the given cryptocurrency to sabotage the blockchain.
The same way a Proof of Work system requires the hacker to have control of more than 51% of the total computational power of the blockchain, a Proof of Stake system can only be hacked if the stakeholder holds more than 51% of the entire supply of coins on the network. The randomized algorithmic selection process mentioned before, ensures that 51% of the total sum of coins will never be used in the staking process.
Because of Proof of Stake’s less computing intensive model, it requires nearly 99% less energy than a Proof of Work system. It also means that smaller, individual stakeholders have a much higher potential to earn more crypto without possessing computer farms the size of small countries. This makes a Proof of Stake model more enticing to smaller holders.
It’s still early on in the development phase for Proof of Stake, so there is bound to be some security concerns surround the staking model, however it is quickly becoming the preferred option among professional investors and cryptocurrency pundits alike.
Best Crypto To Buy

Now you have a good grasp of what cryptocurrency is and how you actually buy it, it’s time to start finding the best crypto coins to invest in. With so many to choose from, it can be a literal minefield, even for the most experienced investor.
This is why each month, we bring you three of the best crypto coins to buy as chosen by our experts. Essentially, make sure it’s a page you have bookmarked.
How To Avoid Tax On Cryptocurrency?

The Australian Tax Office (ATO) has made it clear that you need to declare tax on crypto in Australia if you make a profit from selling it.
The official information says, “Bitcoin is neither money nor a foreign currency, and the supply of bitcoin is not a financial supply for goods and services tax (GST) purposes. Bitcoin is, however, an asset for capital gains tax (CGT) purposes.”
Essentially, if you’re making a profit from Bitcoin, even though it’s not recognised as ‘money’ you still need to pay tax on any capital gains, much like selling shares or property.
However, there are strategic ways of spending your crypto that could help you to avoid paying taxes come the end of the tax year. To find out how make sure to check out our full guide to crypto tax in Australia.
Crypto Wallets
If you own cryptocurrency, no matter if it’s a large amount or a small amount, then you need a crypto wallet to store it. Although, technically, a crypto wallet doesn’t store your crypto but instead, stores the unique address where your cryptocurrency assets can be found on its respective blockchain.
Check out our complete guide to the best crypto wallets in Australia to learn more about them and find out which crypto wallet is best for you.
Crypto Staking

Crypto staking can be likened to putting your money into a high-interest savings account. Essentially, in return for locking up your crypto coins – which helps keep a certain blockchain running – you can earn rewards that, for the most part, are a lot higher than the interest rate offered by banks.
If you want to understand what crypto staking is and learn how much money you can make from staking your crypto, then be sure to check out our full in-depth guide.
Crypto Cards

Thanks to the sheer popularity of cryptocurrency, the world’s major banks have sat up and taken notice and started producing crypto cards in the form of debit, credit and prepaid cards.
These cards allow you to spend your crypto coins by converting your owned coins into fiat currency whenever you use them at a card payment terminal.
The post What Is Cryptocurrency, How Does It Work & Which Crypto Should You Buy? appeared first on DMARGE.
0 Commentaires